<BOJ> 13913 자바(숨바꼭질4)
2024. 7. 20. 21:35ㆍAlgorithm/BOJ
반응형
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/13913

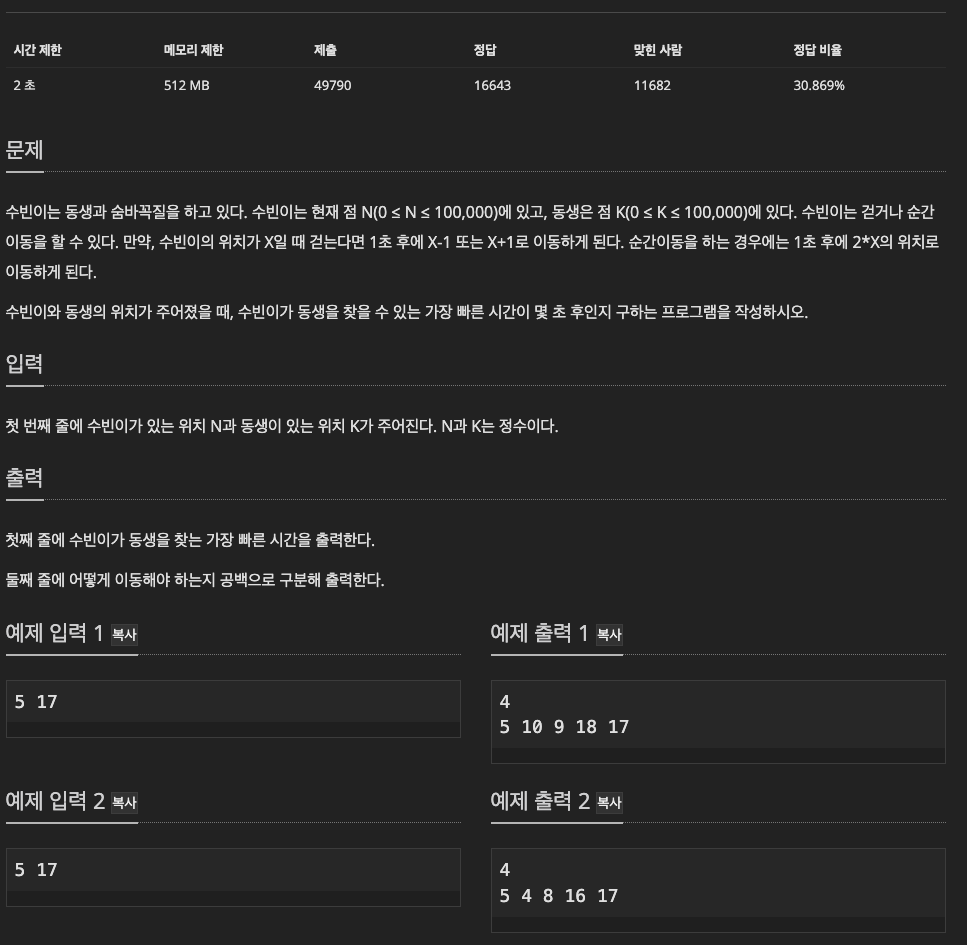
BFS를 활용해야 하는 문제이다.
처음 풀이했던 코드가 틀려서 뒤적거리다 보니 접근법이 이상했나 보다.
[첫시도 - 시간초과]
package algorithms.src;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class B13913_숨바꼭질4 {
static int S, E, CNT;
static int[] route;
static int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static boolean[] visited;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static PriorityQueue<Edge4> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
S = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
route = new int[100001];
visited = new boolean[100001];
bfs();
System.out.println(sb);
}
private static void bfs() {
q.add(new Edge4(S, 0, route));
route[0] = S;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Edge4 edge = q.poll();
if(edge.vertex == E) {
sb.append(edge.time).append("\n");
for(int i = 0; i < edge.time; i++) {
sb.append(edge.rt[i]).append(" ");
}
sb.append(E);
return;
}
visited[edge.vertex] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int nV = 0, nT = 0;
int[] cloneRt = edge.rt.clone();
switch (i) {
case 0:
if(S > E) continue;
nV = edge.vertex * 2;
nT = edge.time + 1;
cloneRt[nT] = nV;
break;
case 1:
nV = edge.vertex - 1;
nT = edge.time + 1;
cloneRt[nT] = nV;
break;
case 2:
nV = edge.vertex + 1;
nT = edge.time + 1;
cloneRt[nT] = nV;
break;
}
if(nV > 100000) continue;
if(nV < 0 || visited[nV]) continue;
q.add(new Edge4(nV, nT, cloneRt));
}
}
}
}
class Edge4 implements Comparable<Edge4> {
int vertex;
int time;
int[] rt;
public Edge4(int vertex, int time, int[] rt) {
this.vertex = vertex;
this.time = time;
this.rt = rt;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge4 o) {
return this.time - o.time;
}
}
굳이 PQ구현도 필요 없고 더 간단하게 풀 수 있는 문제였다.
5에서 17까지 가는 경로를 보면, [5 - 4 - 8 - 16 -17] 순으로 4초 동안 이동한다.
이를 알고리즘으로 구현해 보면, 이동할 때마다
1) 부모노드가 무엇인지 기억하고
2) 17(도착노드)을 만났 을 때 역으로 부모노드를 따라가다가
3) 시작 노드를 만났을 때 시간과 경로를 출력해 주면 된다.
[풀이 코드]
package algorithms.src;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class B13913_숨바꼭질4 {
private static int s, e;
static int MAX = 100000;
static int[] parent = new int[MAX+1]; // 부모 노드를 담아줌. 첫 테스트 케이스가 100000인지 MAX로 해주면 런타임 에러 (ArrayIndexOutOfBounds) 발생
static boolean[] visited = new boolean[MAX+1];
static Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
s = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
e = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
q.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
bfs();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(e);
int time = 0;
for (int i = e; i != s;) {
list.add(parent[i]);
time ++;
i = parent[i];
}
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(time);
for (int i : list) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
private static void bfs() {
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int current = q.poll();
for (int next : new int[]{current - 1, current + 1, current * 2}) {
if (next >= 0 && next <= MAX && !visited[next]) {
parent[next] = current;
visited[next] = true;
if (next == e) return;
q.add(next);
}
}
}
}
}
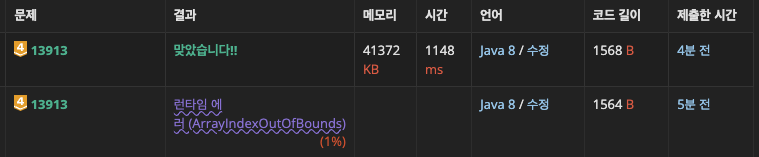
[결과]
* 주의사항
위 주석에도 쓰여있지만 첫 테스트케이스가 100000인지 배열크기를 100000으로 설정해놓으면
런타임 에러 (ArrayIndexOutOfBounds) 발생한다.
static int[] parent = new int[MAX+1]; // 부모 노드를 담아줌.
static boolean[] visited = new boolean[MAX+1];
반응형
'Algorithm > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| <BOJ> 14502 자바 (연구소) (4) | 2024.07.20 |
|---|---|
| <BOJ> 16235 자바 (나무 재테크) (1) | 2024.07.20 |
| <BOJ> 5427 자바 (불) (2) | 2024.07.13 |
| <BOJ> 16236 자바 (아기상어) (0) | 2024.07.13 |
| <BOJ> 12100 자바 (2048(Easy)) (8) | 2024.07.13 |